
Capturing metadata for GeoNode in QGIS
“Metadata is data about data. It describes the various characteristics of the data, such as the data title, abstract, author, or keywords”
Content objects published and created within GeoNode define and govern platform-specific elements such as the object permissions structure, as well as define a relationship between the object metadata and the object source data.
This ensures that spatial data published to GeoNode is published alongside its metadata, and as GeoNode supports the import and export of various standards-compliant metadata formats, this enables users to generate metadata in external applications.
Whilst GeoNode has the ability to generate metadata, and tools for you to populate it from within the platform, other GIS applications may provide an interface where users can pre-generate full metadata and associate it with a layer during the upload process.
This module will outline how to accomplish this using the QGIS Desktop GIS application.
You try:
Goal: To explore metadata capabilities in QGIS
- Load your Layers into QGIS
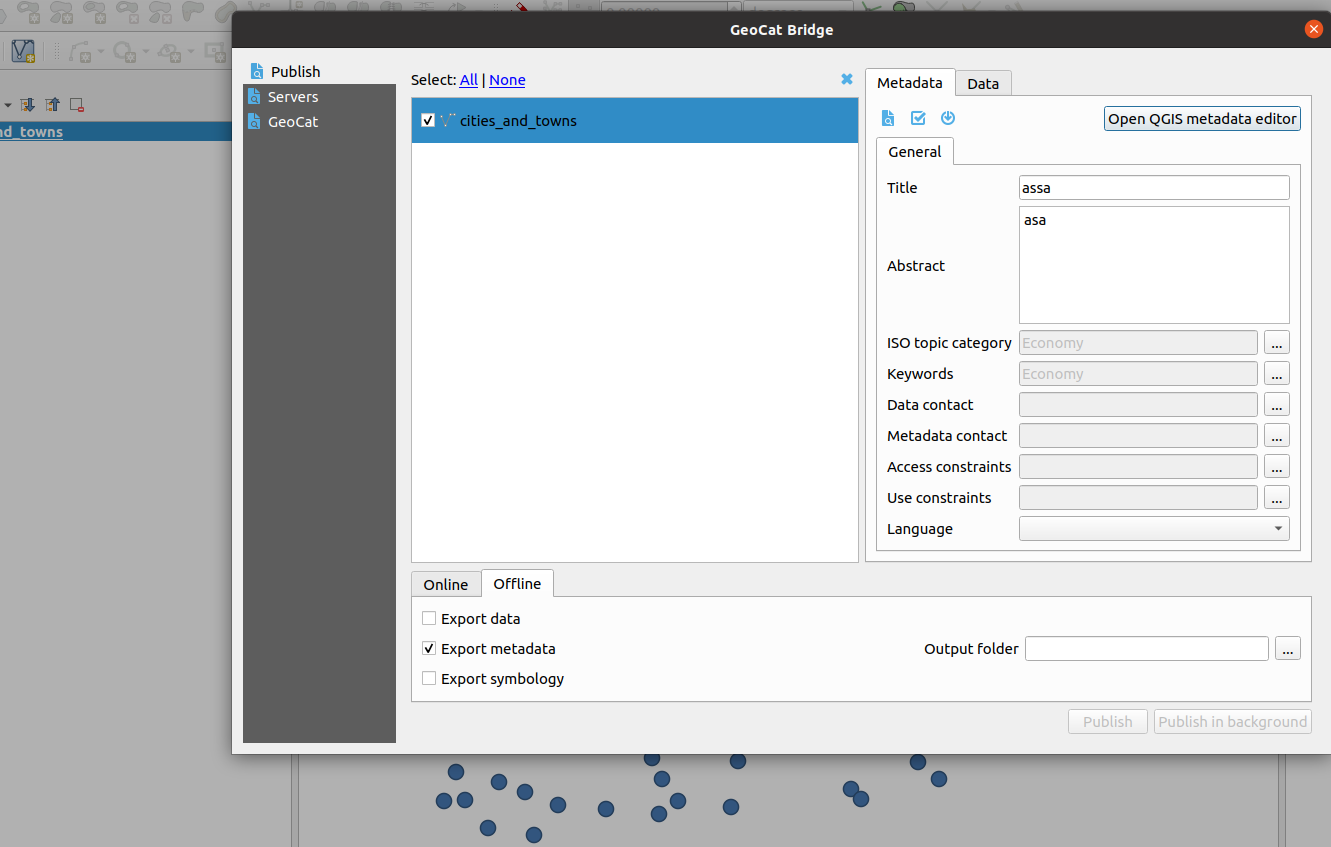
- Install the GeocatBridge plugin by navigating to
Plugins>>Manage and install plugins, and searching for the termgeocat - Open the plugin, and in the Publish tab, populate all metadata for your layer.
- Open the QGIS metadata editor within the plugin dialog
- Validate all the metadata that has been generated
- Select Offline editing and export the metadata
- Export the vector layer onto the disk
- Navigate to GeoNode and upload the vector layer alongside the XML (metadata document)
Please note that if this XML file is to be uploaded and recognised by GeoNode the "metadata" file must be named the same as the layer it is to be applied to - Review the loaded layer and it's metadata on GeoNode
| Name | Expectation |
|---|---|
Layers |
OGR or GDAL data layers |
Metadata tool |
MetaTools plugin |
Keywords tool |
InaSAFE plugin |
Metadata file |
.xml in ISO 19115 format |

More about metadata in external clients
GeoNode supports numerous standards-compliant metadata formats, and these can be attached or uploaded with data after being generated in a variety of external applications such as QGIS, ArcCatalog or similar metadata generation applications.
In QGIS there are various ways to populate metadata, however, the native QGIS metadata editor, available from the metadata tab in the layer properties dialog, does not currently allow users to download metadata in standards-compliant formats and only supports the QGIS specific qmd format. Metadata editing is still possible from within QGIS by leveraging third-party plugins, such as the InaSAFE, GeocatBridge, or Metatools plugins.
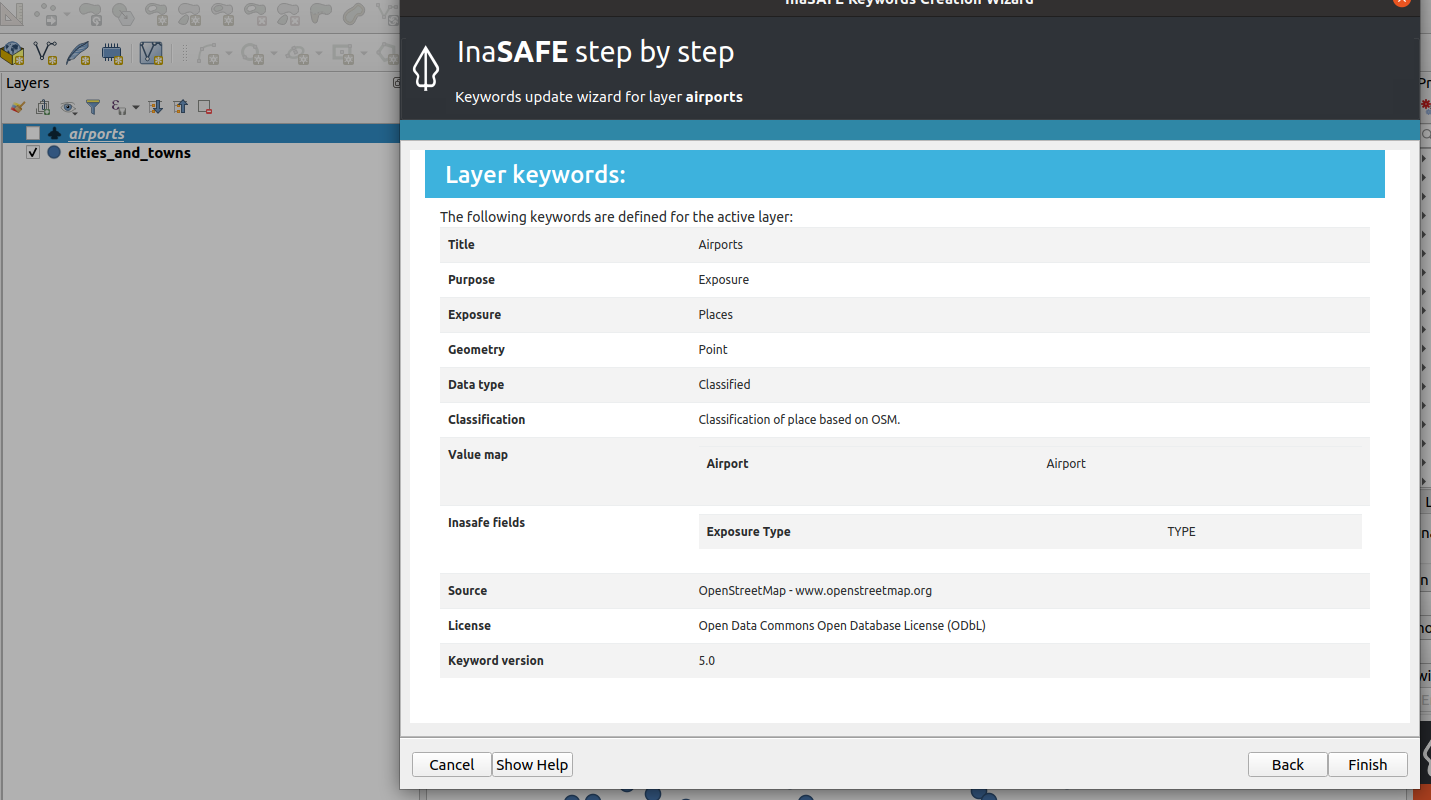
Other third-party tools like InaSAFE are not designed to fully manage the import or export of metadata records, hence there is some learning required to use the tool. When InaSAFE generates metadata it populates only a subset of the metadata fields, including adding the keywords to the Supplemental Data field. Utilizing tools like MetaTools allows users to include additional details about the data within the metadata, so that users might fully understand all data elements.
Richly populated metadata is important for many reasons, including:
- Recording the provenance of the data
- Recording the processing history
- Noting the correct attribution and licensing information
- Providing details of any access constraints
- Providing web service access URLs, publication details, and data endpoints
- Providing contact information and custodianship details
- being interoperable with other ISO 19115 compliant metadata systems
- Compliance with regulatory frameworks and policies, such as the INSPIRE directive used in the EU

Check your knowledge:
-
Why would a user choose GeoCatBridge plugin over native QGIS metadata editor to generate metadata for use in GeoNode:
- QGIS Metadata editor only works with vector layers
- QGIS Metadata editor only produces a subset of the metadata records supported by GeoNode
- QGIS does not export the metadata into a format that GeoNode understands
-
Metadata generated from both InaSAFE and GeoCatBridge can be ingested in GeoNode, despite being produced by different tools. Why is that:
- The metadata contains Keywords and this allows them to be used in GeoNode
- GeoNode does not care about the contents and structure as long as the metadata file has the extension (.xml)
- They all produce metadata that adhere to some common standard

Further reading:
-
INSPIRE Metadata Information https://inspire.ec.europa.eu/metadata/6541
-
Wikipedia Metadata Article https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metadata
